4.2 Operators will first make use of their existing strengths to target new markets
As operators start to plan or deploy their 5G SA networks, they will prioritise the use cases and sectors where they can reap the most immediate gains. In many cases, they will initially focus on building on existing strengths. For example, an operator may already have established partners and relationships in a certain industry (such as automotive), or it may have a strong implementation of a technology (such as augmented reality) that could be applied to new use cases in adjacent industries.
The variety of applications that can be delivered to these existing or adjacent user bases will be increased once an SA network with a cloud-based core and the full range of connectivity capabilities are deployed. This can improve the business case, even for operators that do not venture far into new enterprise markets. They can generate higher levels of usage and adoption by enhancing consumer services with capabilities such as virtual reality.
There will be short-term benefits from harnessing the 5G capabilities that can support use cases in both consumer and industrial environments for those operators that do extend their reach significantly. For example, augmented reality can support consumer applications such as physical/digital shopping, as well as industrial use cases such as digital twins. Some applications that have been developed for a consumer base, such as live events broadcasting, can also be used with a B2B base, such as content providers.
There is a marked contrast between operators’ top use case priorities for 5G NSA (Figure 3) and those for 5G SA (Figure 8). Operators were asked to select their top-three commercial opportunities for the 5G SA era among the same core set of services. Unsurprisingly, merely enhancing the overall MBB experience was a strategic opportunity for far fewer operators (24%). Richer video experiences remained central; they were placed in the top-three by the largest number of respondents (44%). However, in terms of new opportunities, the biggest increase in interest was seen in improved support for AR/VR, cloud gaming and broadcasting (sometimes optimised by dedicated slices).
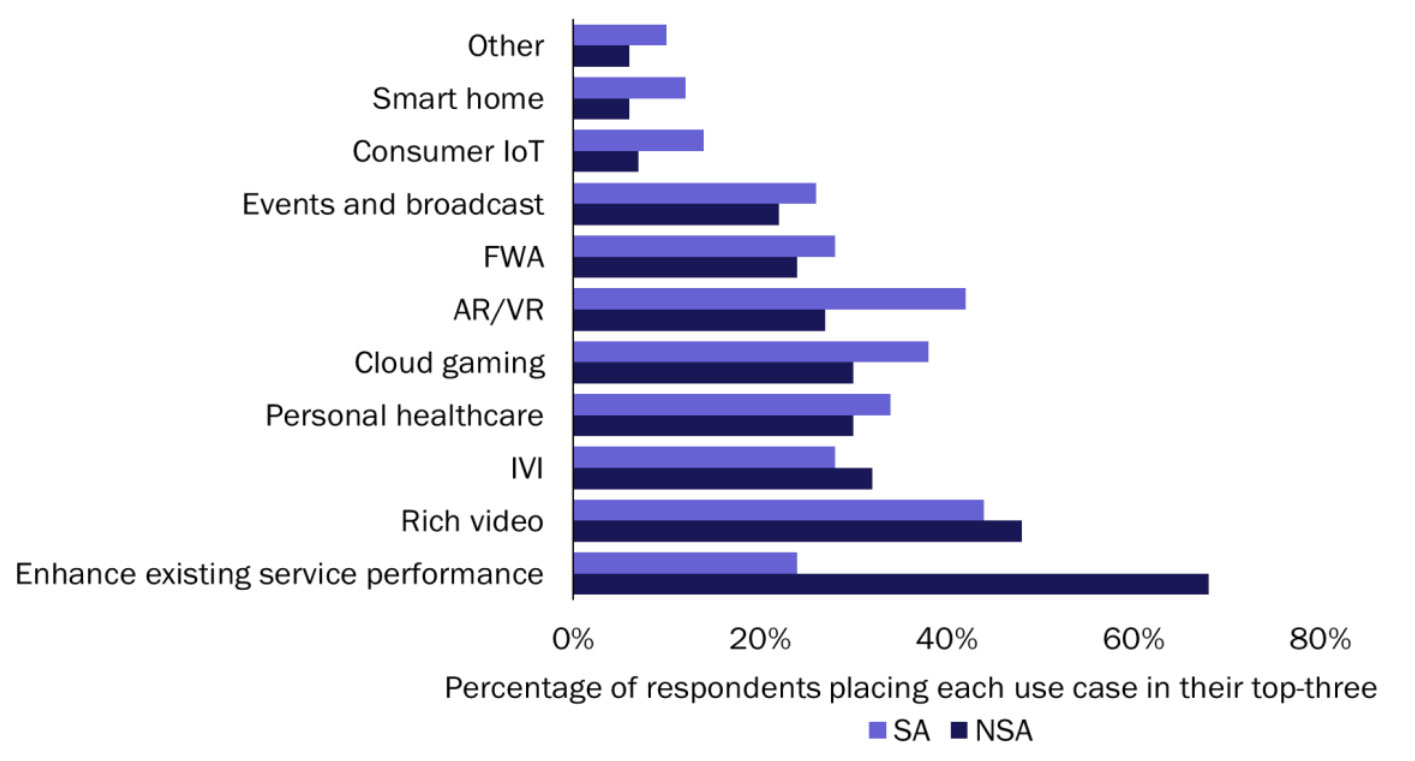 Figure 8: Top-three use cases for the first (NSA) and second (SA) phases of 5G deployment in terms of their importance to the 5G business case, Tier-1 and 2 operators in developed economies, 2Q 2020. Source: Analysys Mason, 2020
Figure 8: Top-three use cases for the first (NSA) and second (SA) phases of 5G deployment in terms of their importance to the 5G business case, Tier-1 and 2 operators in developed economies, 2Q 2020. Source: Analysys Mason, 2020
4.3 Operators are currently making key decisions about the low hanging fruit for B2B 5G services
The biggest gains from the deployment of a full 5G platform will come from the ability to diversify into many industries. Operators vary significantly in terms of the industries that they plan to address and their timelines to do so. Many commercial factors will influence their decision, such as the presence of other competitors, the level of demand for 5G in a given market and their established relationships with partners and potential customers.
Figure 9 highlights this diversity; respondents of our survey were asked whether they planned to address each of 11 selected B2B verticals with 5G services, and if so, in which phase of their deployment they anticipated doing so. As seen in the previous chapter, the verticals that will be commonly targeted in the NSA phase tend to be B2B extensions of consumer-facing markets that are already familiar to many operators (for example, entertainment providers and healthcare professionals).
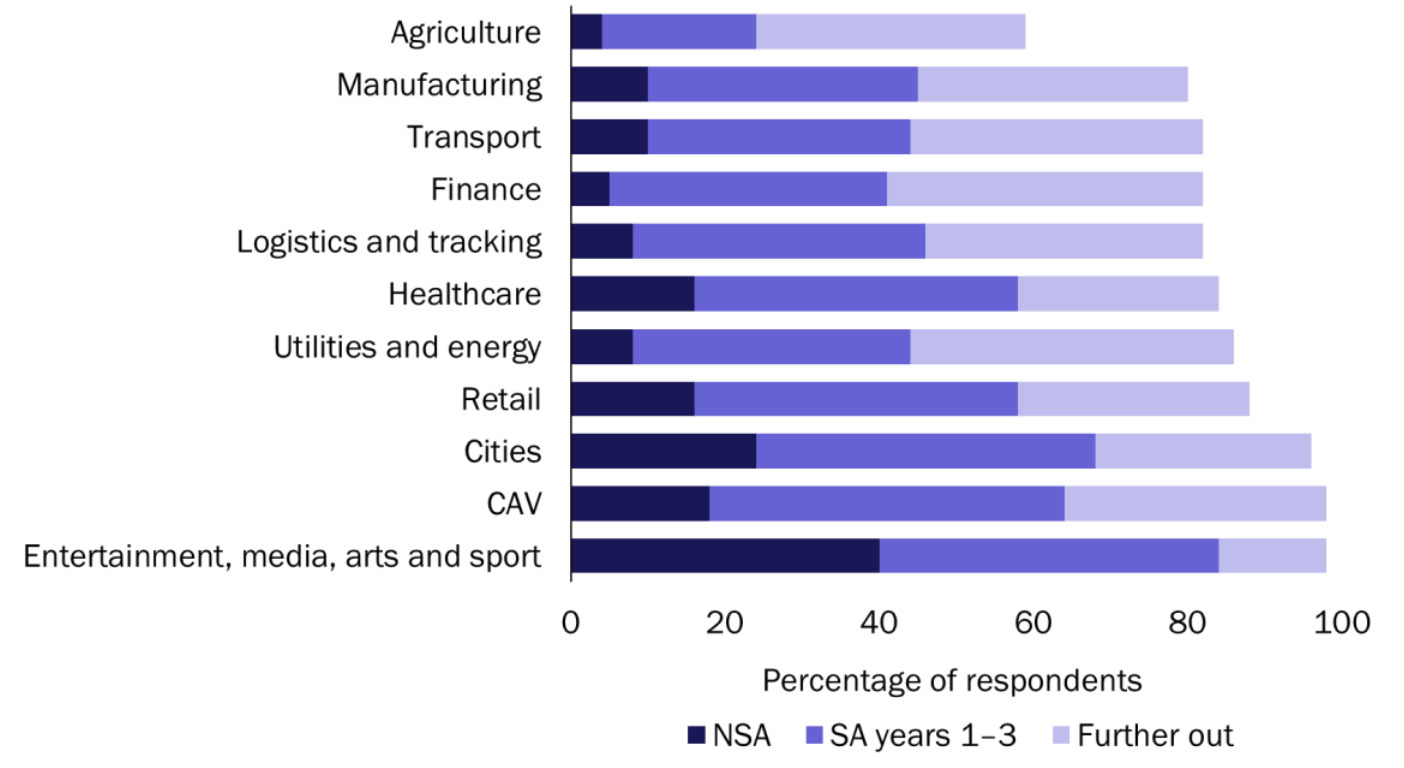 Figure 9. Source: Analysys Mason, 2020
Figure 9. Source: Analysys Mason, 2020
Across the whole 5G era, the sectors that will be addressed by the highest percentage of operators do tend to have a consumer-facing aspect: the leaders are entertainment, media, arts and sport, connected and automated vehicles (CAV), smart cities and retail. More-industrial sectors, which may have less-penetrable ecosystems for operators, will be of very high value to the operators that succeed in building a business there, but will be targeted by a smaller percentage. These sectors include financial services, transportation, utilities, manufacturing and agriculture, all of which will be targeted mainly when an operator has already established a 5G core, often with slicing capabilities.